Automotive Cable & NARVA Part Numbers Explained
— February 08, 2021 | 2 min read
NARVA offers a high-quality cable for all sectors of the automotive market. We use oxygen free copper and RoHS compliant polyvinyl-chloride (V90 PVC) insulation that comply with Australia’s strict standards, plus road train cables that comply with Australian Design Rules, so you know you are using the very best.
While it’s clearly labelled on the outer packaging, plus directly on larger cables, on every product you’ll see a range of markings that give you information about the product. It includes the type of cable (automotive as an example), its colour, dimensions (mm²), length, the part number and amps.
When it comes to amp rating, temperatures have a big part to play here. The Australian standard calls for a cable to be rated with a maximum conductor temperature of 60°C at 25°C ambient. However, it is becoming more common to refer to the JIS or JASO standards for auto cable, which rates the cable with a maximum conductor temperature of 80°C, giving it a higher rating for the same cable.
NARVA Part Numbers
The NARVA part number itself offers more detail than you may think! Take for example part number 5813-7GN:

The first two digits, being “58”, denote a part that falls under our automotive cable category. The third digit (a “1”) refers to the number of wire cores in that particular cable, so we know that this part number is a single core cable (a twin core cable would use the number “2” instead), designed to carry one signal. A twin core cable may be used to carry both the positive and negative signal along two wires inside the same cable. Additional functionality can be added to a circuit by using triple core cable.
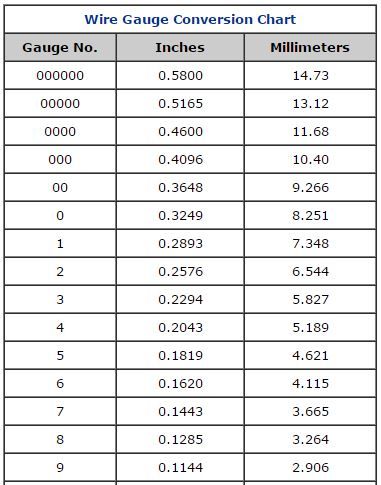
The fourth digit in our part number refers to the diameter of each core in the cable, as measured in mm. In this case, with a “3” digit, the diameter is 3mm. The diameter or thickness of a cable shares an important relationship with the amperage that can pass through safely, without overheating, as well as the maximum length the cable can safely and effectively carry power for. You can find the maximum rated amps for each cable in the NARVA catalogue and on our website, as well as our packaging. Sometimes wire thickness is measured in units known as “wire gauge” and conversion to mm is relatively easy – there are many charts and calculators on the internet, such as below:
Next in our part number is the length of the cable that comes in the pack – most often a 5, 7, 30 or 100 - referring to the length in metres.
Closely followed are two letters that make up either the cable’s colour code or specific application. There are several different colour codes: BK is black, RD red, GN green, YW yellow, OE orange and so forth. Using the right colour cable is important for circuit identification and common practice, for example, the classic “red = positive and black = negative/earth” association. In some cases, the two letters will denote a specific application, such as SP (speaker), DI (double insulated), or HT (high tension) cable. These cables have special properties that make them more suitable for certain requirements.
So it is all there on the package and the cable itself, but NARVA is here to help. You can find more information on NARVA’s extensive range of cables and what will suit your application at www.narva.com.au and within our catalogue (also available on the website).
